
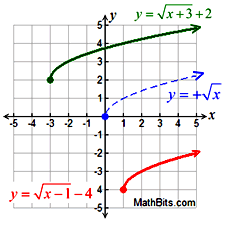
Y = #sqrt(x+2) - 7# First, make a prediction.will the graph be translated right 2 or left 2, up 7 or down 7?įind the domain by setting x + 2 #>=# 0 for starters.Īnd, subtraction of 7, must mean down 7. If you are ready for a challenge, we can try to translate in more than one direction at a time! Adding 3 will raise the graph up, and subtracting 4 will lower the graph by 4 units. The addition or subtraction on the OUTSIDE of the square root function will cause the graph to translate up or down. Now, let's explore how to translate a square root function vertically. This graph will be translated 5 units to the left. Here,’’is the radical symbol used to represent the root of.

Suppose, x is the square root of y, then it is represented as xy or we can express the same equation as x 2 y. Hence, squares and square roots are related concepts. The square root is an inverse method of squaring a number. This implies a horizontal shift/translation of 2 units to the right. Square root of a number is a value, which on multiplication by itself gives the original number. You must set x - 2 #>=# 0, or say that you understand that the square root function has a domain of #x>=2#. So in the end, the definition of the square root as the non-negative (b) so that (b2 x) makes the square root a function. Let's look at the effect of the addition or subtraction. The Graph of the Square Root Function Look at the graph of the square root function below: As you can see, that function only takes non-negative values, and it actually passes the vertical line test, so it is a function. In the case of the square root function, it would look like y = #sqrt(x-2)# or y = #sqrt(x+5)#. In order to translate any function to the right or left, place an addition or subtraction "inside" of the Parent function.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
